Computers and Binary Language
The Computer hardware can understand only the binary language comprising of 0's and 1's.
Bit: It is the smallest unit of data in a computer. A bit has a single binary value either 0 or 1 or simply ON or OFF.
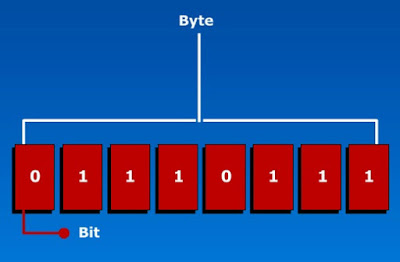
Byte: It is comprised of 8 bits.
Word: A group of 16/32/64 bits (depending on the CPU).
Each number or letter is a combination of 0's and 1's.
For example '69' in binary representation can be written as 69 base10 = 01000101 base 2
Algorithm
An algorithm is a finite set of instructions performed in a prescribed sequence to achieve a goal, especially a mathematical rule or procedure used to compute a desired result.
or
An algorithm is a step by step, finite sequence of instructions that leads to the performace of a particular task.
Characterstics of an Algorithm
Input: Zero or more inputs are externally supplied.
Output: At least one output is produced.
Definiteness: Each instruction is clear and impeccable.
Finiteness: If we trace out the instructions of an algorithm, in all cases the algorithm terminates after a finite number of steps.
Effectiveness: Every instruction must be very basic, so that it can be essentially carried out, using a pencil and some paper.
An algorithm to display the sum of three given numbers:
Step1: Begin
Step 2: Read three numbers a,b,c
Step 3: Store a+b+c in the sum
Step 4: Display the sum
Step 5: End
An Instance
Step1: Begin
Step 2: given numbers 12, 25, 33
Step 3: sum = 12 + 25 + 33
Step 4: Display "70"
Step 5: End

