- Object diagram is a set of objects and their relationships
- Graphically, a class diagram is a collection of vertices and arcs
Contents
Object diagram contains
- Objects
- Links
- To model a snapshot of a set of objects in a system at a given point in time
- To model an instance of interaction diagrams
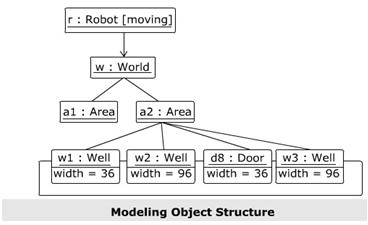
Modeling Object Structure:
- Decide on the mechanism to model
- A mechanism refers to some function or behavior of the system achieved through the interaction of a set of cooperating classes, interfaces, and other things
- Build a collaboration to explain a mechanism
- Find out the classes, interfaces, and other elements that take part in this collaboration and the relationships among them
- Consider one scenario that walks through this mechanism
- Using a snapshot of the scenario, show each object that participates in the mechanism
- Show the state and attribute values of each such object to understand the situation
- Likewise, expose the links among these objects, that represent instances of associations among them
Reverse Engineering
To reverse an object diagram:
- Select the target to reverse engineer
- Usually, the context is inside an operation or relative to an instance of one particular class
- Using a tool or walkthrough freeze execution of a scenario at a certain point in time
- Check out the set of objects that collaborate in that context and depict them in an object diagram
- To understand their semantics better, expose these objects states
- To understand their semantics, find out the links that exists among these objects
- If the diagram becomes complex, simplify it by eliminating objects that are not significant in the scenario
- As necessary, expand the neighbors of the objects and expose the state of each object in more detail
- Structure needs to be added or labeled, which is not clear in the target code
- The missing information explains the design objective