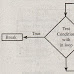
Q35. Explain about break, continue and goto statements (or) Write about jump statements.
Answer:
break Statement 4
The ‘break’ statement performs unconditional jump that terminates or exits from the iteration or switch statement. It
terminates the loop as soon as the control encounters it. And then the control is transferred to the statement that occurs after the
iteration or switch statement. Therefore, it closes the smallest enclosing of do, for, switch or while statements.
Syntax
Example
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>:
int main()
{
int a =1; // variable declaration
and initialization
clrscr()
while (1)
{
cout <<"
"<<a;
if (a == 15) // checks the value
of a with 15
break; // exit from the loop
a++;
}
getch( );
return 0;
}
Output:

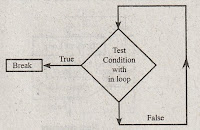
continue Statement
Continue statement is a unconditional Jump statement. It tells the interpreter to continue the next iteration of the loop.
Continue is a keyword used for continuing the next iteration of the loop. Incontrast to the break statement, the continue statement does not exit from the loop but transfers the control to the testing expression (while, do-while) and to the updating expression (for). While and do-while loops can logically act as a jump statement that transfer the control to the end of the loop body. This is because both of these statements transfer their control to two different positions.
Example
#include <iostream.h>
#include <constream.h>
main()
{
int i=0;
clrscr( );
do
{
i=i+1;
if(i>5 && i<7)
continue;
cout <<“The value of i is :”
<< i <<endl;
}
while(i<10);
getch();
return 0;
}
Output

goto Statement
Goto statement performs unconditional jump, thereby changing the actual flow of. program execution. This statement uses label to specify the location where the control has to be transferred (Le., target statement),
Syntax

The label is usually a plain text and is unique. It can be placed at any location within the program.
Example
#include <iostream.h>
#include <constream.h>
void main( )
{
int i=0,s=0;
clrscr( );
sum : s = s+i;
i=i+l;
if(i <= 10)
goto sum;
cout << “Sum of first 10
fate numbers is:”<<s;
getch( );
}
Output