Q40. Explain about default arguments.
Answer:
Default Arguments
Default arguments are the arguments, for which default values are assigned during function declaration. When more than one arguments are not specified in the function call then the compiler provides default values to these arguments in the function prototype.
Handling of default argument requires,
For convenience, the parameters without default values are placed first followed by those with the default values.
Example
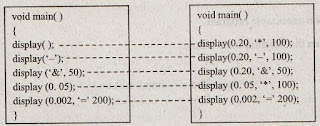
Figure below shows how the calling functions are treated by the preprocessor.
Answer:
Default Arguments
Default arguments are the arguments, for which default values are assigned during function declaration. When more than one arguments are not specified in the function call then the compiler provides default values to these arguments in the function prototype.
Handling of default argument requires,
- Function prototype or function definition
- The knowledge of default arguments prior to function call.
For convenience, the parameters without default values are placed first followed by those with the default values.
Example
void display(double = 0.20, char =
‘*’, int = 100);
void main( )
{
clrscr( );
display( ); //uses default values
for all the arguments
display(‘-’); /Auses default
values of the first and third arguments
display('&', 50); // use
default value for the first argument
display(‘&’, 50); //uses
default values for second & third arguments
display(0.002, ‘=’, 200);
//ignores the default value
getch( );
}
void display(double d, char ch, int
i)
{
int a;
cout << endl;
a=0;
while(a < i)
{
cout << ch << i;
a++;
}
}
When the compiler encounters the first call to the function display( ) in the main program, it replaces all the missing arguments with default arguments and treats the function as,
display(0.20, *, 100);
When the second call to the function i.e., display(‘-’); is involved then the compiler replace the missing argument with the default value for the first and third arguments and ignores the default value for the second argument and treats the function as,
display(0.20, ‘-’, 100);
Similarly, it treats all the calling functions in the same way by supplying the default values for the missing arguments.Figure below shows how the calling functions are treated by the preprocessor.
void display (double = 0.20, char = ‘*’, int = 100); //function prototype

Figure: Treatment of Function Calls by Preprocessor

