catch( type argument)
{
//code
}
A catch block takes an argument as an exception. These arguments specify the type of an exception that can be handled by the catch block. When an exception is thrown the control goes to catch block. If the type of exception thrown matches the argument then the catch block is executed, otherwise the program terminates abnormally. If no exception is thrown from the try block then the catch block is skipped and control goes immediately to the next statement following the catch block.
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std:
int main()
{
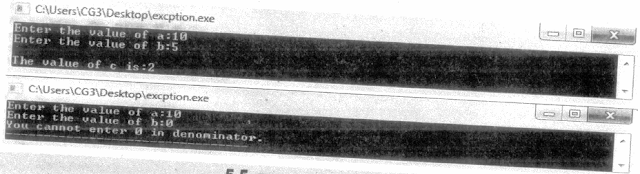
int a, b, c;
cout <<"Enter the value of a: ";
cin:>>a;
cout "Enter the value of b:;
cin>>b;
try
{
if(b)=0)
{
throw b;
}
else
if (b < 0)
{
throw "Negative denominator not allowed";
}
c = a/b;
cout<<"\nThe value of c is:"
<<c;
}
catch(int num)
{
cout<<"You cannot enter
"<<num<<" in denominator.";
}
}