2. Multiple Inheritance
It refers to the process of deriving a child class from many base classes. It consists of a single Hence class but multiple base classes as shown in below figure,
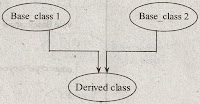
Figure: Multiple Inheritance
Syntax
class Base_class1
{
};
class Base_class2
{
------
};
class Derived _class : Visibility
Base class1, Visibility Base_class2
{
------
}
Example
class Cars
{
//body
}
class Bikes
{
// body
};
class Speed : public Cars, public
Bikes
{
// body
};
Program
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h> ;
class Basel
{
protected:
int x;
public:
void get_x(int);
void show_x();
};
class Base2
{
protected:
int y;
public:
void get_y(int);
void show_y()
};
class Derived : public Base1,
public Base2
{
public:
void show(void);
};
void Base1::get_x(int p)
{
x=p;
}
void Base1::show_x()
{
cout<"x="<<x<<endl:
}
void Base2::get_y(int q)
{
y=q
};
void Base2::show_y()
{
cout<<“y="<<y<<endl;
}
void Derived::show(void)
{
cout<<“x="<<x<<endl;
cout<<“y="<<y<<endl;
cout<<“x+y”<<(x+y)<<endl;
}
void main( )
{
Derived d;
clrscr();
d.get_x(5);
d.show_x();
d.get_y(10);
d.show_y();
d.show();
getch();
return;
}
Output